The field of quantum computing has changed not only into a more of an experimental idea that can be found in research laboratories but also into a technology with practical industrial consequences. Recent advances in quantum computing 2024 show apparent gains in qubit stability, logic circuit fidelity, hardware scalability and cloud accessibility on an enterprise scale.
The technological innovation of the past decades has been driven by classical computers based on transistor-based architecture. However, the traditional computing platforms would not handle the computationally intensive workloads which are exponential (such as molecular simulations, optimization problems, cryptographic modeling, and artificial intelligence training workloads).
The solutions to these issues can be found in quantum computing which are based on the laws of quantum mechanics, that is:
- Superposition
- Entanglement
- Quantum interference
Unlike binary bits used in classical computing systems, quantum machines operate using qubits, which can simultaneously exist in multiple computational states. This allows quantum processors to execute complex calculations across parallel probability distributions rather than sequential processing pathways.
Understanding the Role of Qubits in Modern Quantum Systems
A classical bit exists in either a 0 or 1 state at any given moment. In contrast, a qubit can exist in a superposition of both states simultaneously.
This enables:
- Parallel computational modeling
- Rapid optimization problem solving
- Enhanced machine learning processes
- High-dimensional simulation capability
However, qubits are extremely sensitive to:
- Thermal fluctuations
- Electromagnetic interference
- Environmental noise
- Decoherence
Until very recently, adding more qubits to a system prompted more error propagation as opposed to better performance. A change in the focus of increased qubit count to improved quantum error correction protocols to increase logical qubit efficiency was one of the biggest in 2024.
Key Quantum Computing Breakthroughs in 2024
The most notable breakthroughs in 2024 were concentrated across the following technological domains:
- Logical qubit construction
- Fault-tolerant system design
- Error correction protocols
- Neutral atom computing platforms
- Hybrid classical-quantum processing models
Logical Qubits vs Physical Qubits
Logical qubits are composed of multiple physical qubits designed to maintain computational stability against environmental noise.
| Qubit Category | Noise Resistance | Error Correction Capability | Practical Application Readiness |
| Physical Qubits | Low | Minimal | Experimental |
| Logical Qubits | Medium | Significant | Emerging |
| Topological Qubits | High | Advanced | Development Stage |
Redundant qubit innovation The amount of physical qubits needed to run big quantum algorithms goes down because logical qubits, which are more dependable and cost-effective, implement it.
Quantum Hardware Platform Comparison (2024)
Different hardware architectures offer unique trade-offs in performance, stability, and scalability.
| Hardware Platform | Qubit Technology | Coherence Time | Error Rate | Scalability |
| Superconducting Circuits | Josephson Junctions | Low | Medium | High |
| Trapped Ion Systems | Electromagnetic Traps | High | Low | Medium |
| Photonic Systems | Optical Circuits | Medium | Low | High |
| Neutral Atom Platforms | Laser Trapping | High | Low | Very High |
| Topological Qubits | Majorana Particles | Very High | Minimal | Experimental |
Neutral atom quantum computing gained momentum in 2024 due to:
- Parallel qubit manipulation
- Improved coherence time
- Reduced system noise
- Modular scalability
These systems are expected to support larger computational frameworks by 2026.
Quantum Computing Cloud Pricing Comparison
Access to quantum hardware remains predominantly cloud-based due to infrastructure costs associated with:
- Cryogenic cooling
- Electromagnetic shielding
- Quantum processor fabrication
- Error correction circuitry
Annual Quantum Cloud Access Pricing (2024)
| Quantum Service Provider | Entry-Level Cost | Enterprise Cost | Deployment Model |
| IBM Quantum Cloud | $96,000 | $1,000,000+ | Cloud |
| Microsoft Azure Quantum | $10,000 | $500,000 | Hybrid |
| Amazon Braket | $8,000 | $350,000 | Cloud |
| Rigetti Quantum Services | $12,000 | $400,000 | Cloud |
| Neutral Atom Platforms | $150,000 | $2,000,000+ | On-Premise |
Cloud-based access provides the most economically viable entry point for enterprises experimenting with quantum algorithms.
Cost of Building a Private Quantum Computing Infrastructure
Deploying an on-premise quantum computing system involves substantial capital investment.
| Infrastructure Component | Estimated Cost Range |
| Cryogenic Cooling System | $500,000 – $2M |
| Magnetic Shielding | $200,000 – $1M |
| Quantum Processor | $1M – $10M |
| Control Electronics | $250,000 – $900,000 |
| Software Integration | $100,000 – $500,000 |
| Annual Maintenance | $100,000 – $500,000 |
For most enterprises in 2024, cloud-based quantum platforms remain the preferred deployment model.
Global Quantum Computing Investment Distribution (2024)
Sector-Wise Investment Share
| Sector | Investment Share (%) |
| Government | 42% |
| Technology Companies | 31% |
| Startups | 17% |
| Academic Institutions | 10% |
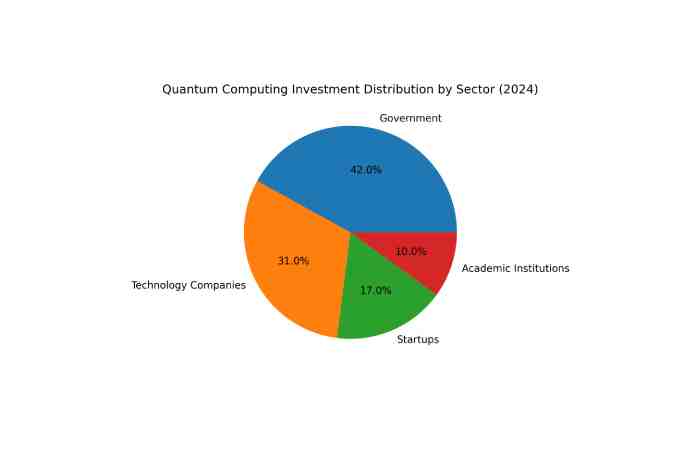
Public sector investment remains dominant due to national security and encryption-related research priorities.
Quantum Computing vs Classical Supercomputers
| Metric | Classical HPC | Quantum Computing |
| Processing Unit | Bit | Qubit |
| Parallel Processing | Limited | Massive |
| Energy Consumption | High | Low |
| Optimization Problems | Time Intensive | Rapid |
| Molecular Simulation | Years | Hours |
| Encryption Analysis | Impractical | Feasible |
| AI Training Efficiency | Moderate | Potentially High |
Quantum computing demonstrates clear advantages in solving NP-hard optimization challenges across:
- Logistics networks
- Pharmaceutical research
- Climate modeling
- Financial risk analysis
- Materials engineering
Enterprise Applications Emerging in 2024
Financial Services
- Portfolio optimization
- Risk simulation
- Fraud detection modeling
- High-frequency trading analysis
Healthcare & Pharmaceuticals
- Drug discovery
- Molecular interaction modeling
- Genetic sequencing optimization
- Vaccine development
Artificial Intelligence
- Quantum neural networks
- Data clustering optimization
- Machine learning acceleration
Transportation & Logistics
- Route optimization
- Traffic simulation
- Supply chain management
Patent Filing Distribution in Quantum Technology (2024)
| Country | Patent Share (%) |
| China | 38% |
| United States | 29% |
| Japan | 12% |
| Germany | 9% |
| South Korea | 7% |
| Others | 5% |
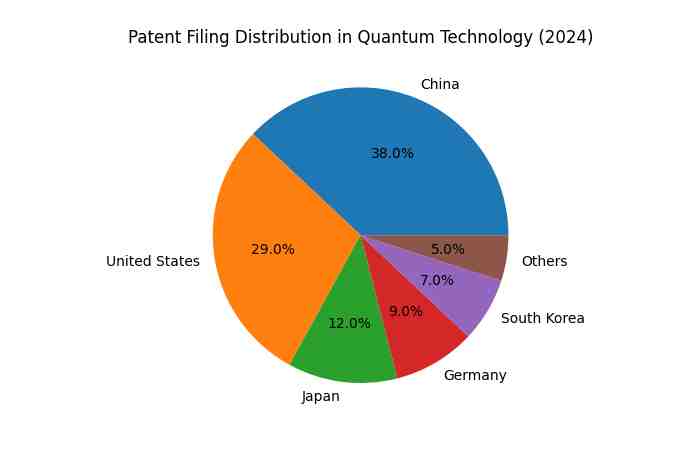
Geopolitical competition in quantum innovation has intensified significantly.
Ongoing Challenges in Quantum Adoption
Despite the latest breakthroughs in quantum computing 2024, several limitations remain:
- Qubit decoherence
- Hardware fragility
- Cooling infrastructure requirements
- Algorithm complexity
- Software ecosystem immaturity
The obstacles persist in slowing mainstream adoption of the enterprise.
Future Market Outlook (2025–2035)
Industry forecasts suggest:
- Quantum computational advantage by 2026
- Fault-tolerant systems by 2029
- Hybrid quantum-AI computing by 2030
The market revenue of global quantum computing will increase by:
- $4 Billion in 2024
- To $72 Billion by 2035
Driven by applications in:
- Financial modeling
- Pharmaceutical simulation
- Advanced manufacturing
- Artificial intelligence
Final Analysis
The latest breakthroughs in quantum computing 2024 represent a structural shift toward scalable and commercially viable quantum architectures. Advances in logical qubit construction, improved quantum error correction protocols, and neutral atom computing platforms have enhanced computational stability and reduced hardware inefficiencies.
Though the large-scale implementation is still limited by infrastructure and the complexity of the algorithm, hybrid quantum-classical systems may be integrated into enterprise cloud computing infrastructure in the next ten years.
Early investment in quantum-ready infrastructure and algorithm development may provide long-term competitive advantages in solving computationally intensive problems across multiple industries.
